User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) design are the cornerstones of any successful digital project. Whether you are developing an e-commerce store, an educational platform, or an ERP system, the user experience ultimately determines the success or failure of the platform. Professional design goes beyond aesthetics; it encompasses the entire user journey, enabling users to reach their goals efficiently and comfortably.
1. User Experience (UX) Fundamentals
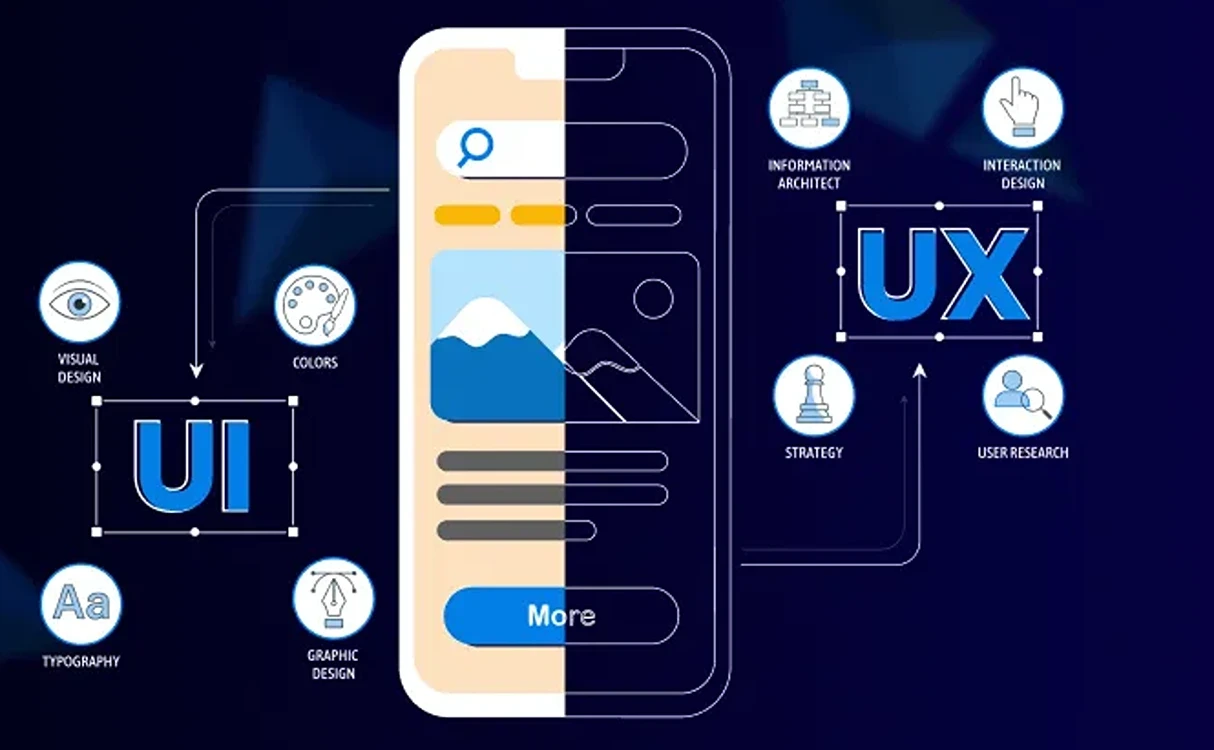
User experience is the customer’s journey within a digital product, encompassing every interaction from entering the website or application to completing the desired goal, whether it’s purchasing a product, completing a course, or entering data into a system.
1.1 Understanding Users
- Research and Analysis: Before starting the design, it is essential to understand users’ needs, behaviors, and preferences. Tools like Hotjar and Google Analytics help track user behavior and analyze their journeys.
- User Personas: Creating profile templates representing different types of users helps guide design decisions realistically.
1.2 Simplifying the User Journey
- Analyze each step the user takes within the app or website.
- Remove obstacles that cause confusion or frustration.
- Practical example: In Al-Mudarrib Al-Lughawi Platform, we simplified access to lessons and quizzes so that students could navigate easily without long searches.
1.3 Usability
- Design should be intuitive, minimizing the need for instructions.
- A clear user experience reduces abandonment rates for actions such as checkout or course registration.
2. User Interface (UI) Design
UI is what the user sees and interacts with; it is the visual aspect of the digital experience.
2.1 Simplicity and Clarity
- Use consistent colors and readable fonts.
- Avoid cluttering information and options, as complexity confuses users.
- Helpful tools: Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch for creating interactive and flexible interfaces.
2.2 Interactivity and Flexibility
- Design smooth interactions, such as clear buttons, seamless navigation, and user-friendly notifications.
- Examples: In the O9medical website, we created a smooth browser experience for visitores, with smart tools to enhance engagement.
2.3 Responsive Design
- Ensure a consistent experience across all devices: mobile, tablet, and desktop.
- Testing tools: BrowserStack, Responsinator for evaluating performance on different devices.
3. Tools and Platforms Supporting Designers
- Figma: Interface design, interactive prototyping, and real-time team collaboration.
- Adobe XD: Interactive design with easy client sharing capabilities.
- Sketch: Ideal for high-quality UI design on Mac devices.
- InVision: Creating interactive prototypes and client experiences before actual development.
- Hotjar / Crazy Egg: Analyzing user behavior on websites or applications.
- Zeplin: Facilitates converting designs into development-ready assets with precise specifications.
4. Practical Experience from Real Projects
- Al-Mudarrib Al-Lughawi Platform: Focused on easy access to content and self-assessment for students, with performance tracking and analysis of strengths and weaknesses.
- Red Crescent and Red Cross Platform: Smooth registration and login experience for trainers and students, with smart notifications to increase engagement.
- E-commerce stores such as Malmasi and Eva Beauty: Designed simple shopping interfaces with streamlined checkout steps to ensure higher conversion rates and reduced cart abandonment.
Conclusion
Professional digital experience design requires integrating user understanding, interface simplicity, interactive design, and device responsiveness. Modern tools help designers create realistic, scalable designs and collaborate efficiently with development teams.
Real success in digital design comes when users feel comfortable and able to achieve their goals quickly—whether they are students, shoppers, or employees using an enterprise system daily.
 English
English
 العربية
العربية

Add New Comment